OSS Telecom
What is OSS?
Operations support systems (OSS) are a collection of software applications designed to manage and support the operational activities of a telecom provider.
It works in tandem with Business Support Systems (BSS) in supporting telecom business activities.
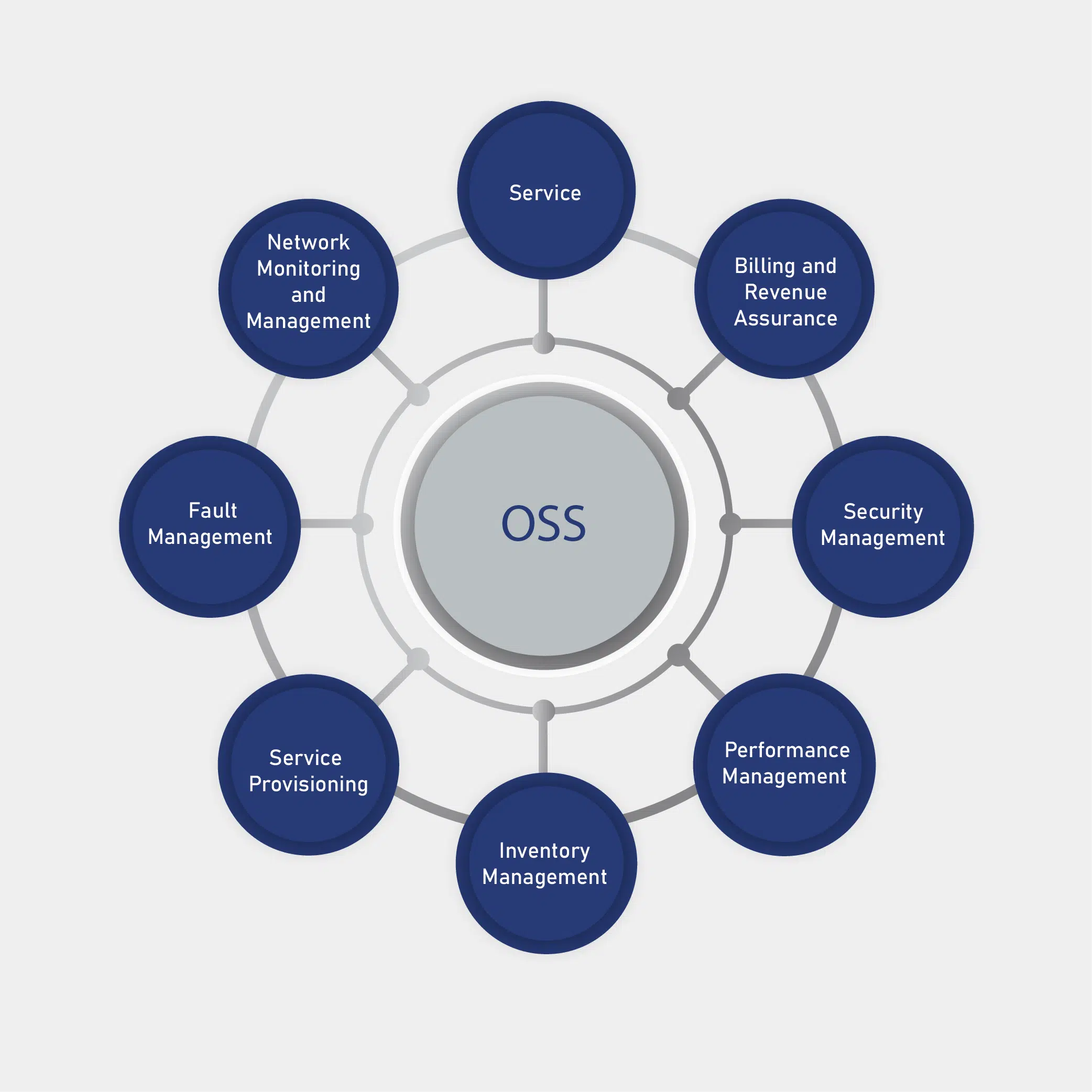
Features of OSS:
In the telecommunications industry, Operation support systems encompass various features that facilitate the management and operation of telecommunications networks. Here are some key features commonly found in OSS for telecom:
- OSS helps gain insights into customer behavior, via collection and evaluation of smart data, rather than big data.
- It works to transform the big data gained from the operational sources, into smart data.
- OSS is uniquely positioned to broker the integration between various Network data sources and usage data (charging data).
- It is flexible and agile in responding to market needs.
- Capable of processing high volumes of data from a high number of individual and diversified sources at the same time.
- It is an integral part of the telecom operators marketing strategy.
Use cases of Operation Support Systems:
-
Network Monitoring and Management
The system provides tools for real-time monitoring and management of network elements, including switches, routers, base stations and transmission equipment. This includes monitoring network performance, availability and fault detection to ensure optimal network operation.
-
Fault Management
OSS includes features for detecting, diagnosing and resolving network faults and performance issues. It provides alerts and notifications for abnormal conditions, facilitates fault isolation and supports troubleshooting to minimize service disruptions.
-
Service Provisioning
It enables the automated provisioning and activation of services for customers. This includes the configuration of network resources, such as bandwidth allocation, service activation and subscriber provisioning, to support new service deployments or modifications.
-
Inventory Management
OSS maintains an inventory of network assets, including hardware devices, software components and logical network elements. It tracks the location, status and configuration of these assets to support network planning, provisioning and maintenance activities.
-
Performance Management
Operation support systems collect, analyze and report on performance data from network elements, to assess overall network health and performance. This includes monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs), identifying trends and optimizing network capacity and performance.
-
Security Management
It includes features for managing security policies, user access control and security event monitoring within the network environment. It helps ensure the confidentiality, integrity and availability of network resources and data.
-
Billing and Revenue Assurance
OSS solutions provide Billing and Revenue Management Systems integration to support accurate billing and revenue assurance processes. They provide data for usage tracking, rating and billing reconciliation to ensure that customers are billed correctly for the services they receive.
-
Service Quality Management
Operation support system includes tools for monitoring and managing service quality parameters, such as call quality, latency and packet loss. It helps ensure that Service Level Agreements (SLAs) are met and enables proactive management of service quality issues.
Conclusion:
From network monitoring and fault management, service provisioning and performance optimization to providing real-time insights, automating processes and facilitating efficient resource allocation, it ensures the smooth operation and reliability of telecommunications services.
Operations Support Systems enable telecom operators to deliver high-quality services, minimize downtime and meet the ever-changing demands of customers in today’s rapidly changing digital environment.
These unique capabilities of the Operation Support Systems, collectively allow telecommunications operators to efficiently manage their networks, deliver high-quality services to customers and ensure the reliability and performance of their telecommunications infrastructure.
